Input Tax Credit
Introduction
The world of Value Added Tax (VAT) can be complex, but understanding how to effectively manage your Input Tax Credit (ITC) can lead to significant savings for your business & it’s rules are governed by VAT Act, 2052 in Nepal.
The process of setting off the Input VAT from the Output VAT before making payments to the Inland Revenue Department (IRD) is known as the offsetting of VAT or Input Tax Credit. This process is essential for businesses to reduce their tax liability and remain compliant with local tax regulations.
Please note that the materials & resources we have used in this blog has been borrowed from Business Taxation Course & Financial Reporting Course.
Types of Tax Credit
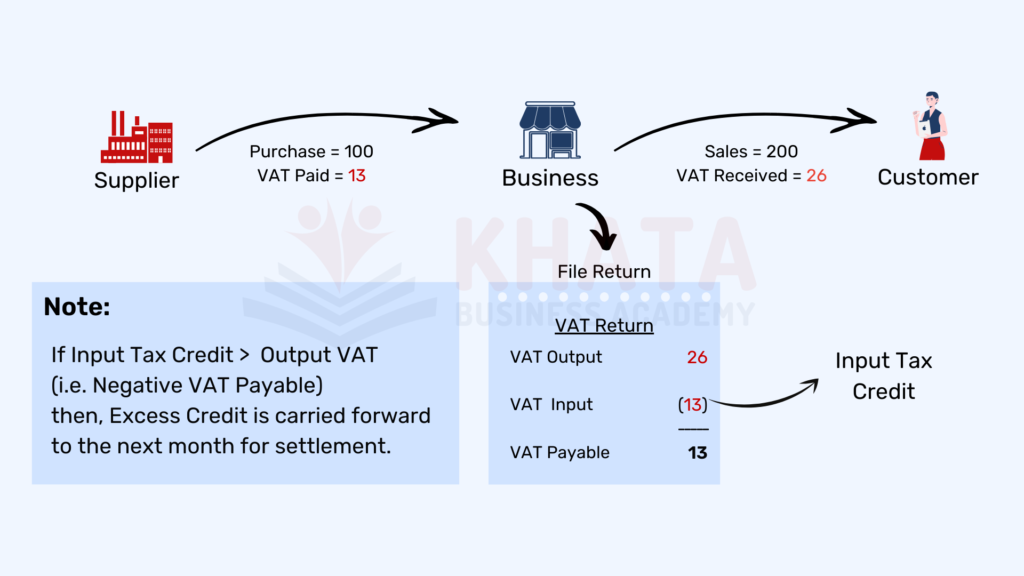
There are 4 types of tax credit which are as follows:
- Full Tax Credit
- Partial tax Credit
- Proportionate Tax Credit
- No Tax Credit
Full Tax Credit
In Nepal, a Full Tax Credit allows a registered person to fully set off the VAT paid on purchases if the output is exclusively VAT-attractive. This means that if your business deals solely in VAT-attractive items, you can claim the entire VAT paid on your purchases.
Even if you deal in both VAT-attractive and exempted items, you can still claim full credit for VAT paid on purchases directly related to VAT-attractive items.

Partial Tax Credit
Partial Tax Credit in Nepal applies when only a certain percentage of the VAT paid on purchases can be claimed. For instance, if your business deals exclusively in VAT-attractive items, you can claim only a portion of the VAT paid on certain purchases.
A common example is the purchase of passenger vehicles, where only 40% of the VAT paid can be claimed as a credit.
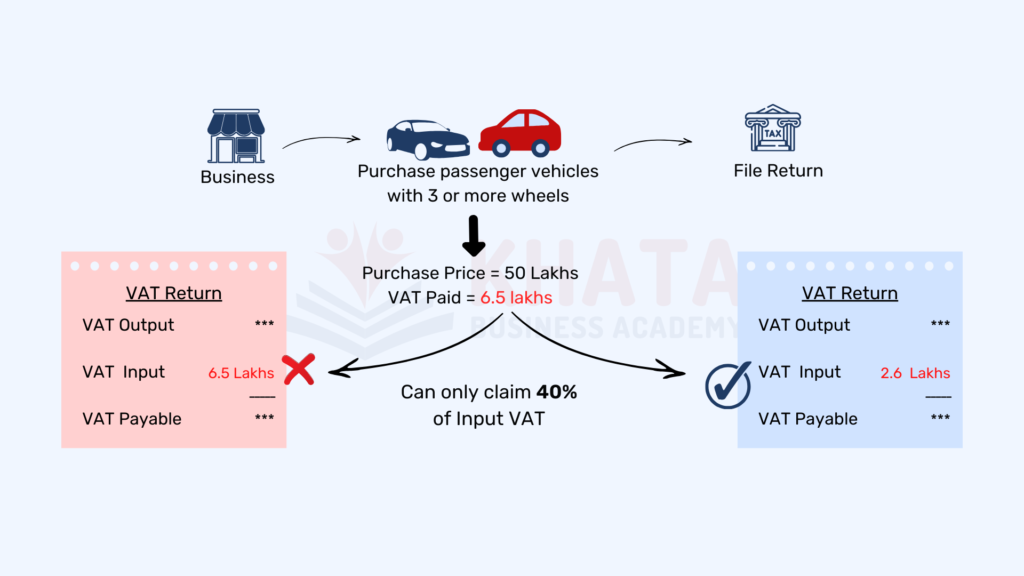
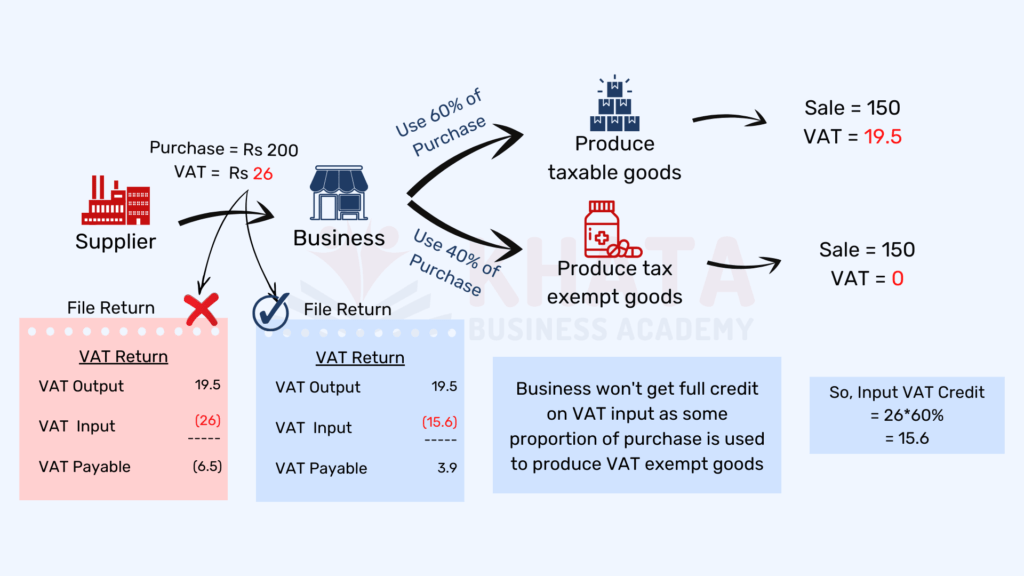
Proportionate Tax Credit
When a business in Nepal deals with both VAT-attractive and exempt items, a Proportionate Tax Credit comes into play. This means that the VAT credit on purchases can be claimed in proportion to the usage of those purchases in producing VAT-attractive items.
It’s a more nuanced approach but can be highly beneficial for businesses with a diverse product range.
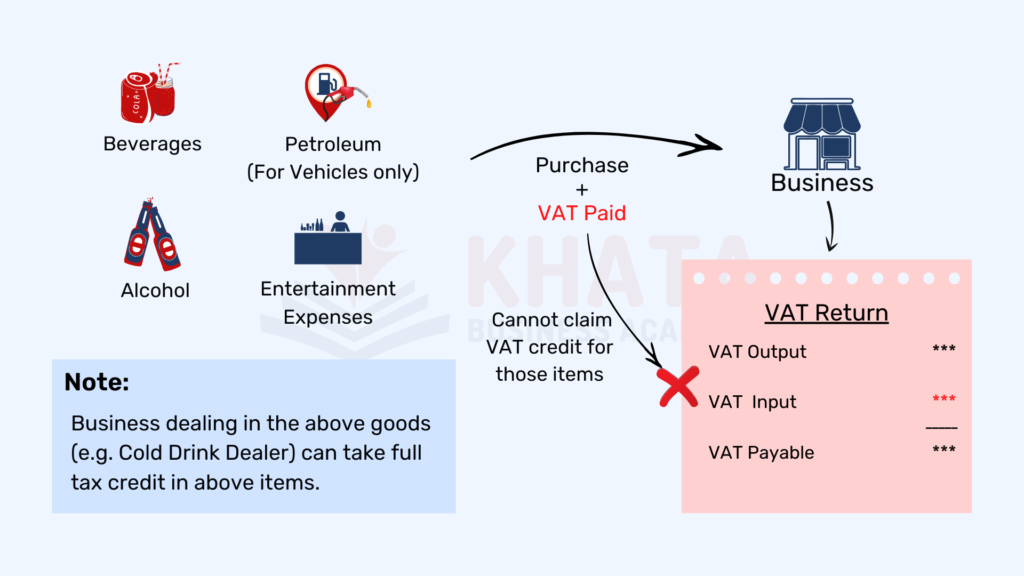
No Tax Credit
In Nepal, certain products and services are not eligible for any input tax credit. Understanding which items fall into this category is crucial to avoid miscalculations and potential penalties.
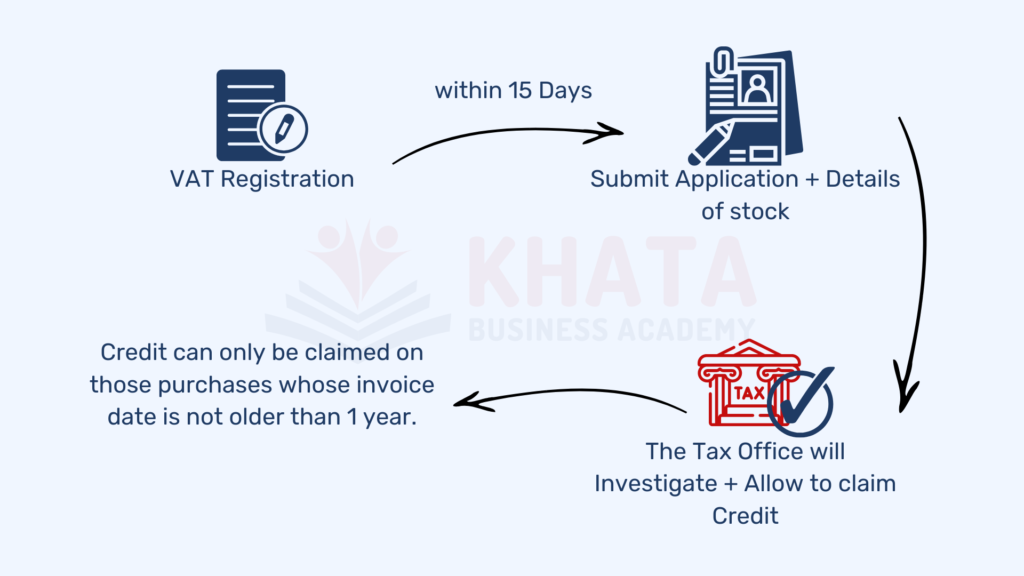
Time Limit to Claim Credit
Input tax credit can be claimed within one year of purchasing or importing goods/services.

Specific Issues
VAT paid on Lost and Damaged goods
In case of lost or damaged goods due to any of the reasons like theft or accident, a person shall file an application to the respective IRO along with evidence within 30 days of happening such events, to write off the goods or sell such goods at a lower than market price. Tax Officer inspects the matter and finalizes the tax credit to be allowed.

Input tax on Stock at the time of registration
When a person is registered for VAT purposes, the person can claim the input tax credit on the goods purchased before the registration and are in stock at the time of registration. The person shall file an application along with details of stock to the Tax Office. Tax Officer will investigate and allow you to claim the credit. Credit can be claimed on those purchases whose invoice date is not older than one year.
Conclusion:
Effectively managing your Input Tax Credit can have a significant impact on your business’s financial health. By understanding the different types of tax credits—Full, Partial, Proportionate, and No Tax Credit—you can make informed decisions that maximize your savings and ensure compliance with Nepal’s VAT regulations.
How to Learn Advanced Accounting & Taxation Skills from Khata Business Academy:
Khata Business Academy offers three interactive online courses that can help you learn and prepare Tax Returns, Financial Reports including Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss, Cash Flow and Financial Projections:
Business Taxation Course
Led by CA Gunjana Manandhar, this course covers practical taxation aspects for accountants, including VAT, TDS, and Income Tax. It uses interactive modules and templates, equipping you with the knowledge and skills required to handle taxation issues effectively, a crucial part of an Accounts Manager’s role.
You can access the course through this link: https://khataacademy.com/np/courses/business-taxation-course/
Financial Reporting Course
Taught by CA Bipin Lamsal, this course is specifically designed to help you become an Accounts Manager by learning about transaction, taxation, managerial, financial, and projection reports preparation skills. The comprehensive coverage of financial reporting is key for anyone aiming to manage accounts at a high level.
You can access the course through this link: https://khataacademy.com/np/courses/financial-reporting-course/
NFRS (Nepal Financial Reporting Standard) For Accountant's Course
This course, instructed by CA Bishal Bhattarai, is tailored for Accounts Managers who want to develop advanced analytical financial skills using NFRS. Understanding NFRS is vital for accurate financial reporting and compliance in Nepal, making this course particularly valuable for aspiring Accounts Managers.
You can access the course through this link: https://khataacademy.com/np/courses/nfrs-for-accountants/